Introduction to Beta-Caryophyllene
Beta-caryophyllene, a naturally occurring terpene found in various aromatic plants such as black pepper, cloves, and cannabis, stands out for its unique chemical profile and ability to interact with the endocannabinoid system. This interaction highlights its significance not only within the cannabis industry but also across various traditional and modern applications.
Beta-Caryophyllene in Cannabis
Within the cannabis community, beta-caryophyllene is revered for contributing to the rich, spicy, and woody aromas of certain strains. It is distinctive among terpenes for its ability to bind directly with CB2 receptors in the body, associated with anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. This capability suggests a profound impact on the physiological experiences attributed to cannabis, enhancing its appeal in both recreational and medicinal contexts.
Interaction with the Endocannabinoid System
Beta-caryophyllene is particularly notable for its interaction with the endocannabinoid system, primarily through its affinity for the CB2 receptor. Unlike many terpenes, beta-caryophyllene acts as a dietary cannabinoid, potentially influencing bodily processes that regulate inflammation and pain. This interaction is not considered to invoke psychoactive effects, as it does not bind significantly with the CB1 receptors located in the brain, which are responsible for cannabis's psychoactive effects. The engagement with CB2 receptors is of interest for its potential to contribute to the feelings of well-being and calmness, without the psychoactivity associated with THC.
Broad Spectrum of Beta-Caryophyllene Benefits
Beyond its significance in the cannabis industry, beta-caryophyllene has a wide range of applications in various other fields.
Culinary Uses
In the food industry, beta-caryophyllene enriches flavors with its spicy notes, making it a favorite in culinary creations that seek a hint of earthiness.
Cosmetic and Personal Care Products
The cosmetic industry values beta-caryophyllene for its soothing properties and its efficacy in skincare formulations, where it is utilized for its fragrance and potential skin-conditioning benefits.
Traditional Remedies
Historically, plants containing beta-caryophyllene have been staples in herbal medicine, cherished for their therapeutic properties.
Natural Sources of Beta-Caryophyllene
While its presence in cannabis is well-recognized, beta-caryophyllene is also abundant in:
- Black Pepper: Known for its robust flavor and benefits.
- Cloves: Used for their potent spice and traditional medicinal value.
- Rosemary: Often found in culinary and therapeutic preparations.
- Hops: Integral to the brewing of beer, contributing aromatic depth.
- Basil: Adds to the herb’s spicy-sweet fragrance profile.
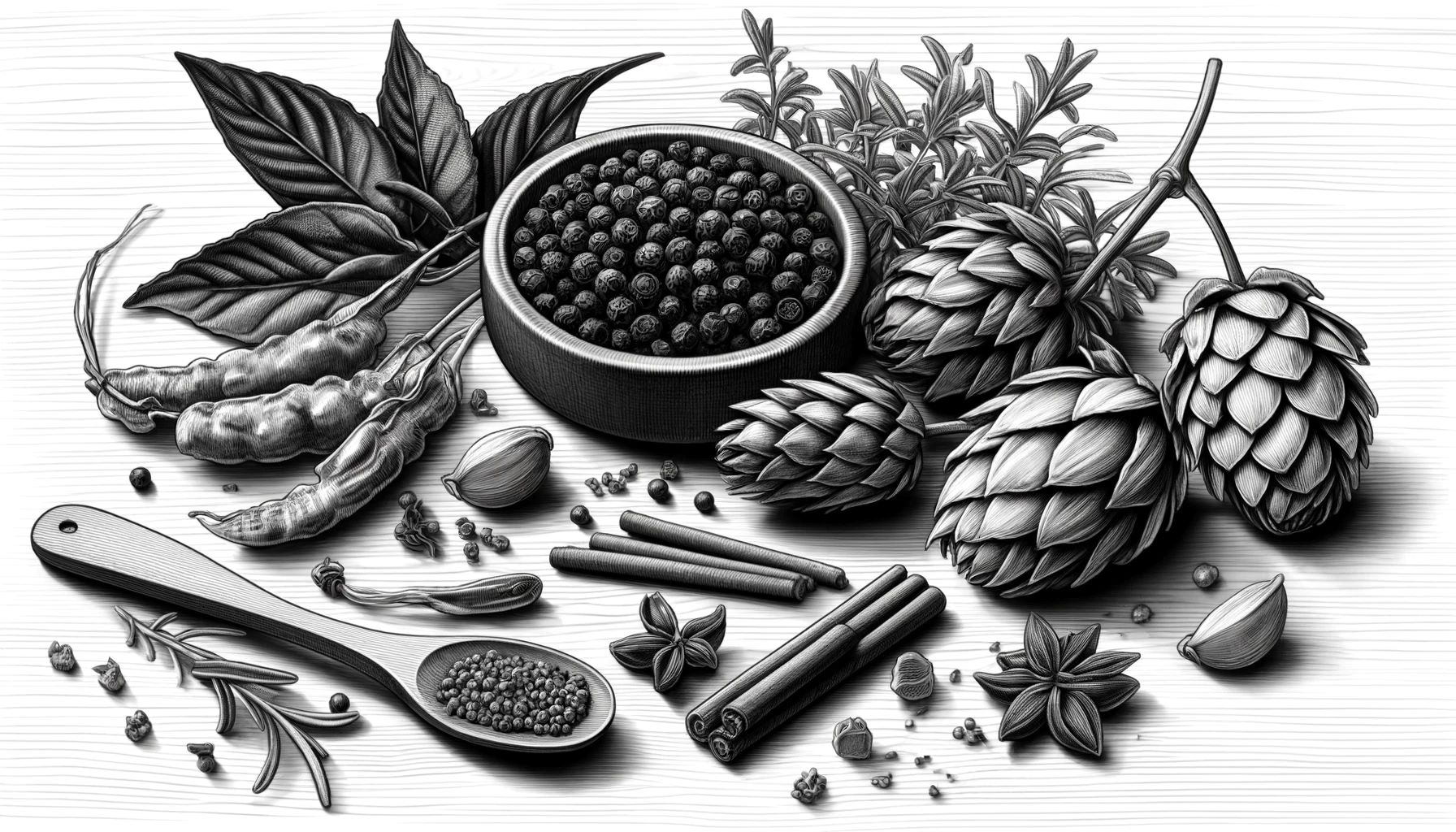

These plants not only contribute rich flavors and aromas but also enhance the therapeutic potentials of the products they inhabit.
The Evolution and History of Beta-Caryophyllene
Beta-caryophyllene has played a significant role throughout history, deeply rooted in the traditions and practices of various cultures around the world. Its journey begins with its natural occurrence in plants, where it serves a critical function in protecting these plants from environmental stresses and pests. This protective quality has not only ecological implications but also practical applications in traditional herbal remedies.
In ancient times, plants rich in beta-caryophyllene were often utilized for their robust flavors and preservative properties. Historical records indicate that spices like black pepper and cloves were highly valued in trade not just for their culinary uses but also for their utility in food preservation and medicine. These spices were among the first forms of natural medicine, used to treat a range of ailments from toothaches to digestive issues, largely due to their content of potent terpenes such as beta-caryophyllene.
Furthermore, beta-caryophyllene's role extends into the spiritual and ritualistic practices of many cultures. For instance, in traditional Ayurvedic medicine, it has been used to balance the doshas — particularly vata and kapha — helping to manage pain, inflammation, and digestive health. Similarly, Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) incorporates cloves and black pepper, both rich in beta-caryophyllene, in various formulations to harness their supposed therapeutic properties, which were thought to influence vitality and health.

Over the centuries, as trade routes expanded, so too did the knowledge of beta-caryophyllene's properties. It became a staple in the medical chests of European explorers and settlers, often used in crude forms for its antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties. The industrial era saw the distillation and more refined applications of essential oils containing beta-caryophyllene, which were used in the burgeoning perfume industry as well as in more scientifically informed medical practices.
Today, the historical and cultural significance of beta-caryophyllene-rich plants continues to influence modern herbalism and natural product formulations. As we uncover more about its biochemical actions through contemporary scientific methods, the rich tapestry of its past provides a colorful backdrop to its modern applications. This deep historical context not only enriches our understanding of beta-caryophyllene but also highlights its enduring relevance in human society.
The Future of Beta-Caryophyllene
As the cannabis industry continues to mature and expand, the role of beta-caryophyllene and other terpenes in shaping the consumer experience is likely to become increasingly important. Further research into the synergistic effects of beta-caryophyllene and other cannabis compounds may uncover additional therapeutic applications, potentially leading to new product formulations and usage patterns.
Beyond the cannabis realm, beta-caryophyllene's versatility ensures that it will continue to be a valuable and widely used ingredient in various consumer goods, from personal care products to food and beverages. As consumer demand for natural, plant-derived compounds grows, the demand for beta-caryophyllene and other terpenes may continue to rise, driving innovation and new applications.
Conclusion
Beta-caryophyllene is a multifaceted terpene that transcends traditional botanical roles to emerge as a pivotal component in modern industries. Its ability to integrate into various consumer products, combined with its non-psychoactive interactions with the endocannabinoid system, positions beta-caryophyllene as a key player in the ongoing exploration of plant-derived compounds. As research into its properties deepens and consumer preferences shift towards more natural ingredients, the significance of beta-caryophyllene is set to grow, influencing the development of new products and therapies in the health, food, and cosmetic sectors.